TiO2作为医用植入材料的应用 2024上海医疗设备展Medtec详解
2024-05-24
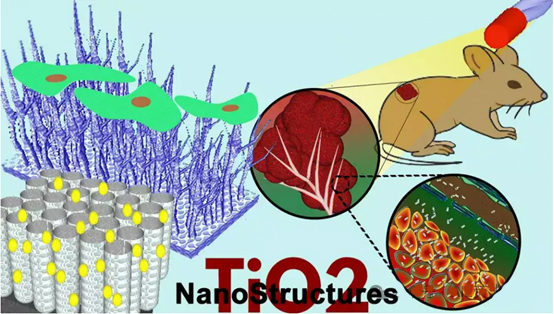
1. TiO2在血液接触材料中的应用
2. TiO2在骨材料中的应用
3. TiO2在生物传感器中的应用
参考文献:
[1] ERIKSSON C, LAUSMAA J, NYGREN H. Interactions between human whole blood and modified TiO2-surfaces: influence of surface topography and oxide thickness on leukocyte adhesion and activation [J]. Biomaterials, 2001, 22(14): 1987-1996.
[2] NAN H, PING Y, XUAN C, et al. Blood compatibility of amorphous titanium oxide films synthesized by ion beam enhanced deposition [J]. Biomaterials, 1998, 19(7): 771-776.
[3] AKO J, BONNEAU H N, HONDA Y, et al. Design Criteria for the Ideal Drug-Eluting Stent [J]. The American Journal of Cardiology,2007, 100(8, Supplement 2): S3-S9.
[4] BRAMMER K S, OH S, GALLAGHER J O, et al. Enhanced Cellular Mobility Guided by TiO2 Nanotube Surfaces [J]. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(3): 786-793.
[5] PENG L, ELTGROTH M L, LATEMPA T J, et al. The effect of TiO2 nanotubes on endothelial function and smooth muscle proliferation [J]. Biomaterials, 2009, 30(7): 1268-1272.
[6] PARK J, BAUER S, SCHMUKI P, et al. Narrow Window in Nanoscale Dependent Activation of Endothelial Cell Growth and Differentiation on TiO2 Nanotube Surfaces [J]. Nano Letters, 2009, 9(9): 3157-3164.
[7] SHUCHMAN M. Trading Restenosis for Thrombosis? New Questions about Drug-Eluting Stents [J]. New England Journal Of Medicine, 2006, 355(19): 1949-1952.
[8] FINN A V, JONER M, NAKAZAWA G, et al. Pathological Correlates of Late Drug-Eluting Stent Thrombosis [J]. Circulation,2007, 115(18): 2435-2441.
[9] YANG Z, ZHONG S, YANG Y, et al. Polydopamine-mediated long-term elution of the direct thrombin inhibitor bivalirudin from TiO2nanotubes for improved vascular biocompatibility [J]. Journal Of Materials Chemistry B, 2014, 2(39): 6767-6778.
[10] DAI S, JIANG L, LIU L, et al. Photofunctionalized and Drug-Loaded TiO2 Nanotubes with Improved Vascular Biocompatibility as a Potential Material for Polymer-Free Drug-Eluting Stents [J]. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2020, 6(4): 2038-2049.
[11] OH S, DARAIO C, CHEN L-H, et al. Significantly accelerated osteoblast cell growth on aligned TiO2 nanotubes [J]. Journal Of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2006, 78A(1): 97-103.
[12] WEBSTER T J, ERGUN C, DOREMUS R H, et al. Specific proteins mediate enhanced osteoblast adhesion on nanophase ceramics [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2000, 51(3): 475-483.
[13] YAO C, SLAMOVICH E B, WEBSTER T J. Enhanced osteoblast functions on anodized titanium with nanotube-like structures [J]. Journal Of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2008, 85A(1): 157-166.
[14] BAE I-H, YUN K-D, KIM H-S, et al. Anodic oxidized nanotubular titanium implants enhance bone morphogenetic protein-2 delivery [J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2010, 93B(2): 484-491.
[15] MAHYAD B, JANFAZA S, HOSSEINI E S. Bio-nano hybrid materials based on bacteriorhodopsin: Potential applications and future strategies [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 225:194-202.
[16] ESTEVEZ M C, OTTE M A, SEPULVEDA B, et al. Trends and challenges of refractometric nanoplasmonic biosensors: A review [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2014, 806: 55-73.
[17] LEE Y-L, LO Y-S. Highly Efficient Quantum-Dot-Sensitized Solar Cell Based on Co-Sensitization of CdS/CdSe [J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2009, 19(4): 604-609.
[18] ZHAO W-W, MA Z-Y, YAN D-Y, et al. In Situ Enzymatic Ascorbic Acid Production as Electron Donor for CdS Quantum Dots Equipped TiO2 Nanotubes: A General and Efficient Approach for New Photoelectrochemical Immunoassay [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(24): 10518-10521.
[19] FAN D, WU D, CUI J, et al. An ultrasensitive label-free immunosensor based on CdS sensitized Fe–TiO2 with high visible-light photoelectrochemical activity [J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2015, 74: 843-848.
文章来源:
作者:












